The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. It is located near the optic nerve. The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused, convert the light into neural signals, and send these signals on to the brain for visual recognition.
The retina processes light through a layer of photoreceptor cells. These are essentially light-sensitive cells, responsible for detecting qualities such as color and light-intensity. The retina processes the information gathered by the photoreceptor cells and sends this information to the brain via the optic nerve. Basically, the retina processes a picture from the focused light, and the brain is left to decide what the picture is.
Due to the retina's vital role in vision, damage to it can cause permanent blindness. Conditions such as retinal detachment, where the retina is abnormally detached from its usual position, can prevent the retina from receiving or processing light. This prevents the brain from receiving this information, thus leading to blindness. Consult with Dr. Sonia Maheshwari Kothari is a Retina specialist in Ghatkopar, Mumbai with over 8 years of experience in medical, laser and surgical management of Vitreoretinal disorders.
A. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy, also known as diabetic eye disease (DED) is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes mellitus. It is a leading cause of curable blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy affects up to 80 percent of those who have had diabetes for 20 years or more.At least 90% of new cases could be reduced with proper treatment and monitoring of the eyes. The longer a person has diabetes, the higher his or her chances of developing diabetic retinopathy.
RISK FACTORS
All people with diabetes are at risk – those with Type I diabetes and those with Type II diabetes. The longer a person has had diabetes, the higher their risk of developing some ocular problem.
Pregnancy might exacerbate the condition and hence it is recommended to have a through eye examination if a diabetic female is pregnant.
How many types of Diabetic Retinopathy are there?
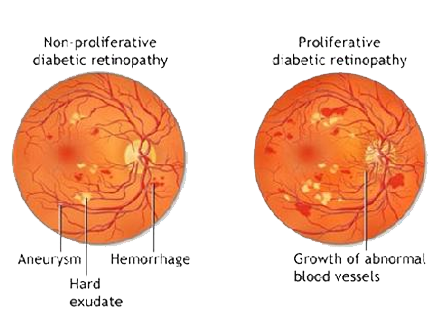
The two types of diabetic retinopathy are Proliferative diabetic retinopathy and Non Proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
New, fragile blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina. These new blood vessels are called neovascularization, and can lead to serious vision problems, because the new vessels can break and bleed into the vitreous. When the vitreous becomes clouded with blood, light is prevented from passing through the eye to the retina.
Types : The two common types of macular degeneration are "dry" and "wet."
This can blur or distort vision and frequently causes sudden and severe loss of vision. The new blood vessels can also cause scar tissue to develop, which can pull the retina away from the back of the eye. This is known as retinal detachment, and can lead to blindness if untreated. In addition, abnormal blood vessels can grow on the iris (the colored part in the front of the eye), which can lead to severe glaucoma.
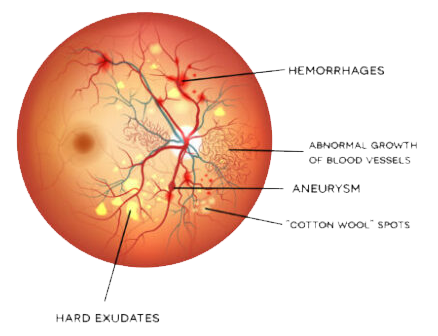
Background or nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy - blood vessels in the retina are damaged and can leak fluid or bleed. This causes the retina to swell and form deposits called exudates.
Many patients may not notice any change in their vision when they develop this early form of the disease, but it can lead to other more serious forms of retinopathy that severely affect vision. Fluid collecting in the macula is called macular edema and may cause difficulty with reading and other close work.
What is the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Good control of diabetes with intensive management and control of blood sugar will delay, and possibly prevent, both the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy. Patients with diabetic retinopathy frequently need to have special photographs of the retina taken. This series of photos is called fluorescein angiography.
Laser photocoagulation is one of the most common treatments for diabetic retinopathy. Focal photocoagulation consists of laser directed at the retina to seal leaking blood vessels in patients with background diabetic retinopathy. Panretinal photocoagulation consists of laser spots scattered through the sides of the retina to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth (neovascularization) and help seal the retina to the back of the eye in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. This can help prevent retinal detachment. There is little recuperation needed after laser surgery for diabetic retinopathy. Laser surgery may require more than one treatment to be effective.
Vitrectomy surgery is performed for patients with very advanced proliferative diabetic retinopathy or retinal detachment. In vitrectomy, the surgeon removes the blood-filled vitreous and replaces it with a clear solution. This allows light to pass through the clear fluid to the retina, where the images are conveyed to the brain.
Pharmacotherapy : Increasingly, a variety of medications are being used to treat the manifestations of background and proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
These involve intravitreal injections of small amounts of medication into the eye.
The type of retinopathy, as well as the patient's general health and eye structure will determine the kind of treatment needed and the type of anesthesia utilized.
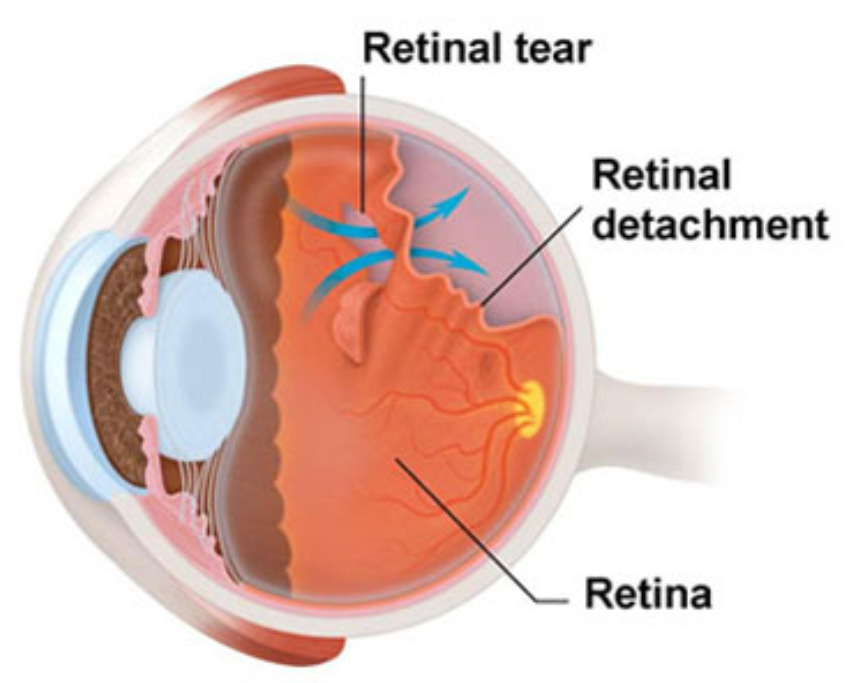
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment describes an emergency situation in which a thin layer of tissue (the retina) at the back of the eye pulls away from its normal position.
Retinal detachment separates the retinal cells from the layer of blood vessels that provides oxygen and nourishment. The longer retinal detachment goes untreated, the greater your risk of permanent vision loss in the affected eye.
Warning signs of retinal detachment may include one or all of the following: the sudden appearance of floaters and flashes and reduced vision. Contacting an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) right away can help save your vision.
Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as:
- The sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes (photopsia)
- Blurred vision
- Gradually reduced side (peripheral) vision
- A curtain-like shadow over your visual field
When to see a doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you are experiencing the signs or symptoms of retinal detachment. Retinal detachment is a medical emergency in which you can permanently lose your vision.
What is the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
Your treatment may involve one or more of these procedures:
- Laser (thermal) or freezing (cryopexy). Both methods can repair a tear if it’s diagnosed early enough. They’re often done in the doctor's office.
- Pneumatic retinopexy. This works well for a tear that’s small and easy to close. Your doctor injects a tiny gas bubble into your vitreous gel. It presses against the upper part of your retina, closing the tear. You’ll need to hold your head in a certain position for several days to keep the bubble in the right place.
- Scleral buckle. Your doctor sews a silicone band (buckle) around the white of your eye (called the sclera). This pushes it toward the tear or detachment until it heals. This band is invisible and is permanently attached.
- Vitrectomy. This surgery repairs large tears or detachment. Your doctor removes the vitreous gel and replaces it with a gas bubble or oil. A vitrectomy also might require you to hold your head in one position for some time.
About 80% to 90% of retina procedures are successful, but you might need to have more than one. It may take several months for your vision to return. Some people don’t get all of their vision back, especially in more severe cases.
A detached retina won’t heal on its own. It’s important to get medical care as soon as possible so you have the best odds of keeping your vision.
For more information & consultation on Retina specialist in Ghatkopar, Mumbai , visit Clear Sight Eyecare & Laser Centre at Ghatkopar East or contact us on 80978 09788 or simply fill in your name and number & one of our team member will get in touch with you soon. Our team of experts along with Dr. Sonia Maheshwari Kothari, Ophthalmologist Eye Surgeon & one of the Best Eye Specialist in Mumbai, will help you out in understanding your problem and guide you through every stage of your treatment. For Clinic direction click here.
